- 2.1.1 Planning Practice - Introduction
- 2.1.2 Planning Practice - Setting goals
- 2.1.3 Planning Practice - Stages of a practice session
- 2.1.4 Planning Practice - Planning appropriate activities
- 2.1.5 Planning Practice - Duration of activities
- 2.1.6 Planning Practice - Using stations and group work
- 2.1.7 Planning Practice-Managing Physical and Psychological Load
- 2.1.8 Planning Practice-adding complexity
- 2.1.9 Review-Reflecting on practice
- 2.1.10 Creating a Positive Environment
- 2.1.11 Providing a Safe Environment
- Follow Up
- 2.3.1 Communicating with Athletes - Listen More, Speak Less
- 2.3.2 “Coaching on the Run” Technique
- 2.3.3 Providing Feedback
- 2.3.4 Changing behaviour with feedback
- 2.3.5 Conducting the Session - Organizing Players into Groups
- 2.3.6 Conducting the Session - Introduce the Activity
- 2.3.7 Conducting the Session - Observe and Give Feedback
- 2.3.8 Adaptive Coaching - Changing Activities to be more effective
- 2.3.9 Adaptive Coaching - Coaching Athletes of Varying Abilities
- 2.3.10 Adaptive Coaching - Including Athletes with a Disability
- Follow Up
- 3.2.1 Productive and reproductive approaches to coaching
- 3.2.2 Different approaches according to age of athlete
- 3.2.3 LTAD - making fun a focus
- 3.2.4 Games-based approach to coaching
- 3.2.5 Differing coaching styles to coaching
- 3.2.6 Communication styles
- 3.2.7 Holistic development - “athlete-centred” approach
- 3.2.8 Holistic development - teaching non-basketball skills
- 3.2.9 Holistic development - developing mindset and resilience
- 3.2.10 Holistic development - developing self confidence
- 3.2.11 Holistic development - developing self control
- Follow Up
- 2.7.1 Basic shooting - introduction
- 2.7.2 Basic shooting - teaching lay-up footwork
- 2.7.3 Basic shooting - foundation for the shot - balanced stance
- 2.7.4 Basic shooting - grip on the ball
- 2.7.5 Basic shooting - "top of the shot" - releasing the ball
- 2.7.6 Basic shooting - shooting off the dribble
- 2.7.7 Basic shooting - jump shot
- Follow up
- 2.8.1 The Importance of the First Step
- 2.8.2 Getting post position
- 2.8.3 Drop step
- 2.8.4 Drop step - counter move
- 2.8.5 Basics of perimeter offence
- 2.8.6 Drive fake moves
- 2.8.7 Shot fake moves
- 2.8.8 Catch and shoot
- 2.8.9 Penetrating off the dribble
- 2.8.10 Activities to practice offence in low post
- 2.8.11 Activities to practice perimeter offence
- Follow-Up
- 1.1.1 Matching up - basic principle of man to man defence
- 1.1.2 Distance from opponent
- 1.1.3 Defending one pass away
- 1.1.4 Flat triangle position
- 1.1.5 Stance - denial or open
- 1.1.6 Moving on the pass
- 1.1.7 Help defence - split line defence
- 1.1.8 Help defence - help to defend dribble penetration
- 1.1.9 Help defence - helping the helper / defensive rotation
- 1.1.10 Defensive communication
- 1.1.11 Transition defence
- 1.1.12 Full court man to man defence
- Follow up
- 1.2.1 Defending off ball screens – “lock and trail”
- 1.2.2 Defending off ball screens – “under”
- 1.2.3 Defending off ball screens – “through”
- 1.2.4 Defending off ball screens – “switch”
- 1.2.5 Defending on ball screens – “under”
- 1.2.6 Defending on ball screens – “over”
- 1.2.7 Defending on ball screens – “through”
- 1.2.8 Defending off ball screens – “switch”
- 1.2.9 Defending on ball screens – “double”
- Follow up
- 2.1.1. Motion offence - 5 out - dribble entry - hand-off
- 2.1.2 Motion Offence - 5 Out - Replacing the Cutter
- 2.1.3 Motion Offence - 5 Out - Purposeful movement - timing and spacing
- 2.1.4 Motion Offence - 5 Out - Ball Reversal
- 2.1.5 Motion Offence - 5 Out - Dribble Penetration - Receivers’ Principles
- 2.1.6 Motion Offence - 5 Out - Dribble Entry
- 2.1.7 Introducing Screens - 5 Out - Pass and Screen Away
- 2.1.8 Scrimmage Activity
- 2.1.9 Allowing Creativity in Decision Making
- Follow up
- 2.2.1 Off Ball Screens - Role of Screener - Setting the Screen
- 2.2.2 Off Ball Screens - Basic Cuts of Screen - Straight Cut
- 2.2.3 Off Ball Screens - Basic Cuts of Screen - Curl Cut
- 2.2.4 Off Ball Screens - Basic Cuts of Screen - Back Cut
- 2.2.5 Off Ball Screens - Basic Cuts of Screen - Flare Cut
- 2.2.6 Off Ball Screens - Role of Screener – Pop or Roll
- 2.2.7 Off Ball Screens - Down screens
- 2.2.8 Off Ball Screens - Up screens
- 2.2.9 Off Ball Screens - Back screens
- 2.2.10 On Ball Screens - Dribbler Options
- Follow up
- 2.3.1 Basic Fast Break - Starting the Break
- 2.3.2 Basic Fast Break - Running Wide Lanes
- 2.3.3 Basic Fast Break - Pass the Ball Ahead
- 2.3.4 Basic Fast Break - 2v1 Fast Break
- 2.3.5 Basic Fast Break - 3v2 Fast Break
- 2.3.6 Basic Fast Break - Moving into Offence
- 2.3.7 Activities to Practice Fast Break Principles
- Follow up
Level 1
2.5.1 Rebounding and Defensive Transition
Offensive Rebounding
In the first place, rebounding requires the players to be in a position where they can actually compete to get the ball. This is instinctive for some players but others, particularly on offence, may not move to a position where they may get the ball. One way that coaches can emphasise this is to award points to players in training activities based upon whether they moved to a rebounding position, not just to the one player that got the rebound.
Secondly, it is important to teach players to anticipate a rebounding situation. Many young players do not get to a rebounding position because they do not anticipate when the shot is to be taken – this is particularly an issue for offensive players. It is important that young players learn to anticipate their teammates’ shots and equally, they must learn that the presence of rebounders is an important aspect in determining whether or not a shot is a good option at that time.
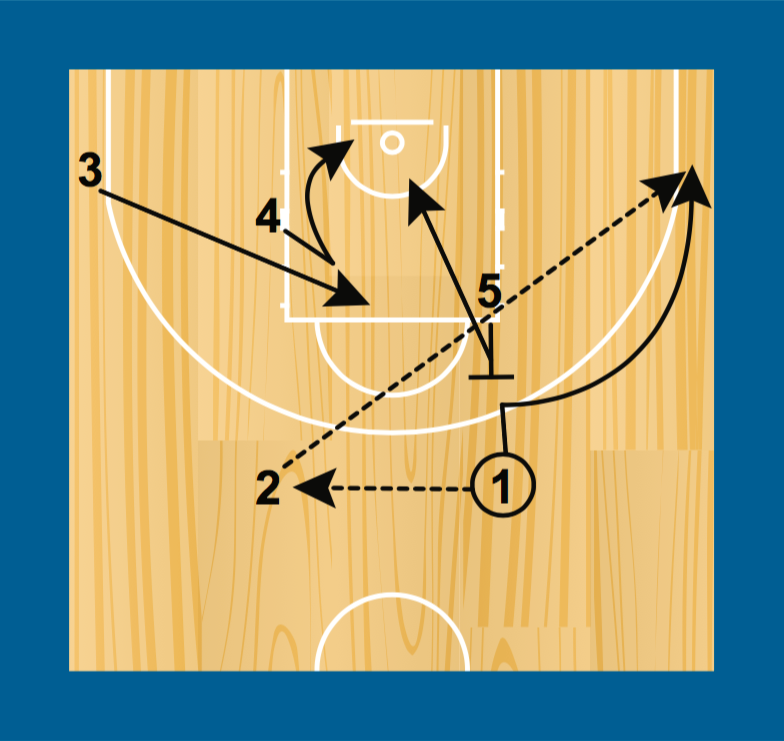
Often in training, coaches will do activities that focus on a particular aspect of the game (e.g. screening and shooting) and the activity then finishes once that is complete (e.g. the shot has been taken). However, to emphasise offensive rebounding, coaches can allow activities to continue until a basket is made or defence controls the ball.
Similarly, offensive rebounding can be added when practicing other offensive moves. The offensive move should not end with the shot but should also end with a score, with players taking offensive rebounding positions.
Coaches should prepare a strategy for both offensive and defensive rebounding.. This includes explaining to players what their responsibilities are and the “pathways” that they may use to contest the rebound. This way, players will consider rebounding as part of the offence or defence and this will also help develop their anticipation of the shot.
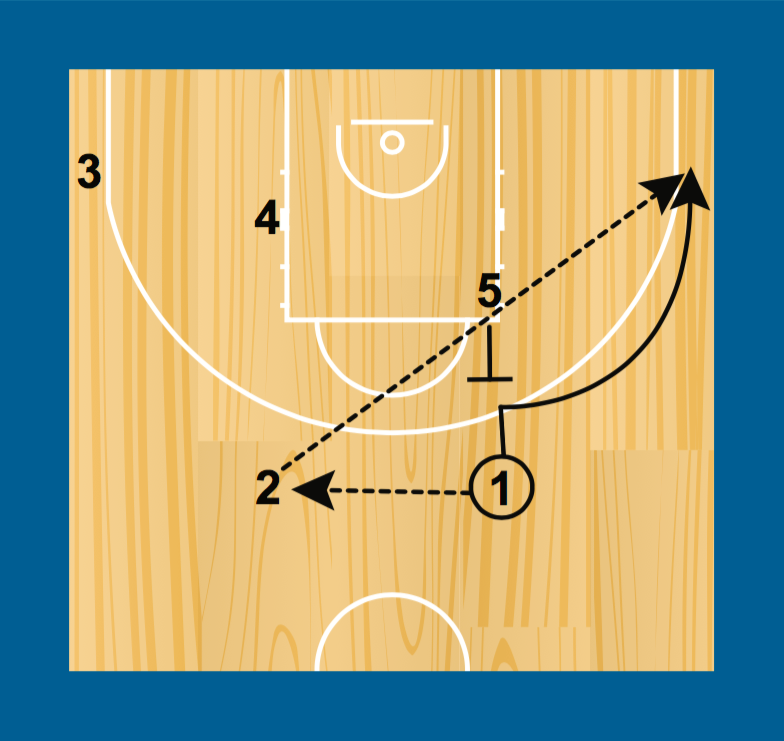
This is an example of a play that a coach may use to get a shot. It finishes when the shot is taken.